Sustainable Architecture: A Holistic Approach to Building Design
Sustainable architecture is a comprehensive strategy for designing buildings and environments that emphasize ecological preservation, social inclusivity, and economic stability. This approach seeks to reduce the environmental footprint of construction from the initial design stage through the building’s entire lifecycle. By focusing on energy efficiency, resource conservation, and climate neutrality, sustainable architecture aims to balance environmental concerns with the well-being of communities and individuals. It promotes culturally sensitive, economically feasible, and socially inclusive design principles to create spaces that ensure equity, comfort, and long-term sustainability for both present and future generations.

Dimensions of Sustainability in Architecture
The three fundamental dimensions—environmental, economic, and socio-cultural—are intricately connected in sustainable architecture, working together to ensure a holistic approach to building design and development.
1. Environmental Sustainability
This dimension emphasizes the protection of natural resources and the reduction of construction’s negative impact on ecosystems. It focuses on using energy efficiently, preserving biodiversity, and minimizing emissions and waste throughout a building’s lifecycle. Sustainable architecture operates within the planet’s ecological limits, using renewable materials and integrating solutions such as renewable energy systems, water conservation, and environmentally friendly building practices.
Principles of Environmental Sustainability:
- Respect the local environment and landscape
- Leverage natural and climatic resources
- Minimize pollution and waste
- Promote human health and well-being
- Reduce the impact of natural hazards
2. Economic Sustainability
Economic sustainability centers on cost-effectiveness and the long-term financial viability of sustainable projects. This involves reducing life-cycle costs, minimizing reliance on subsidies, and encouraging responsible consumption and production practices. Sustainable buildings aim to reduce both initial construction and ongoing operational costs by optimizing resource use. Additionally, they support job creation, promote local businesses, and foster regional economic development through the use of local materials and services.
Principles of Economic Sustainability:
- Encourage self-sufficiency
- Promote local businesses and economies
- Optimize construction efforts and minimize waste
- Extend the lifespan of buildings
- Conserve resources to reduce long-term costs
3. Socio-cultural Sustainability
The socio-cultural dimension prioritizes the well-being of people and communities by enhancing social cohesion and creating safe, inclusive, and culturally meaningful spaces. Sustainable architecture integrates local cultural traditions and practices into building design, ensuring that architecture not only respects but enriches the community’s socio-cultural fabric. It also promotes social equity, public health, and education, contributing to the development of healthy living environments that reflect cultural heritage and identity.
Principles of Socio-cultural Sustainability:
- Protect and enhance cultural landscapes
- Preserve and transfer traditional construction practices
- Encourage creative and innovative solutions
- Recognize intangible cultural values
Conclusion
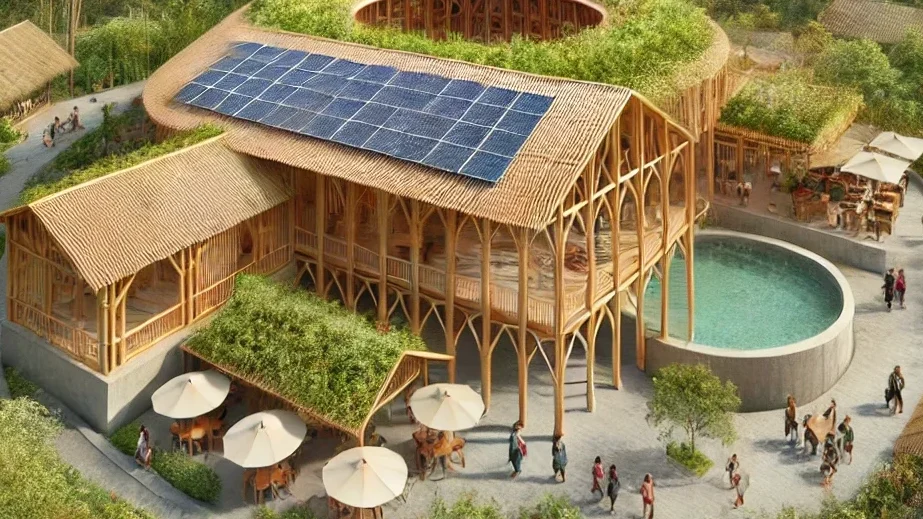

Sustainable architecture represents a balanced fusion of environmental responsibility, economic resilience, and socio-cultural sensitivity. It goes beyond simply reducing environmental impacts to ensure long-term economic viability and social well-being. By balancing these dimensions, sustainable architecture addresses key concerns like energy efficiency, resource conservation, and climate neutrality while fostering local economies, promoting equity, and preserving cultural heritage. This integrated approach ensures that buildings positively impact their environment, provide economic benefits over their entire life cycle, and offer inclusive, healthy, and culturally significant spaces for all.